 |
 |

Preparation resistance grow and continue to evolve, despite the introduction of new antifungal agents, it complicates the treatment of patients. The susceptibility testing in vitro, in many cases, and are used to select the tool and ability to handle a specific infection, but in order to detect the resistance, i.e., perhaps the most important applications, the agent does not work It is a thing to identify. In antimicrobial susceptibility testing in Europe and clinical, standardized methods for reliability in antifungal susceptibility tested in vitro is now available European Commission Institute for Standards Institute and the United States (CLSI) in (EUCAST) on directly below. (In combination with other forms of data) for calculating epidemiology omit values and clinical breakpoints (ECVs) data collected by a standardized test, these are useful. Pathogens (WT) is to be selected to optimize the detection of wild-type strains, they should be species-specific, clinical cut-off value is not broken distribution WT important target species. ECVs are the most sensitive means to identify strains resistant mechanism acquired. Various mechanisms are can lead to acquired resistance of Candida species to obtain a mutation in the gene encoding the (ERG11) target enzyme and azole drugs that induce efflux pump encoded by CDR genes or MDR most often some. Were usually acquired resistance of Candida species to echinocandin mediated by acquisition of point mutations in the gene encoding the major subunit of the target enzyme of the FCC. Preparation resistance is associated with breakthrough infection and poor clinical outcome elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations between prevention and anti-fungal treatment. More and more, and are more resistant to echinocandin antifungal agents and azole isolates of C glabrata Candida due to Candida grab Lata. This situation should be taken further. Aspergillus fumigatus azole resistance rate is low, but the isolates including multidrug-resistant azole part of Europe, reports of emergence of resistance.
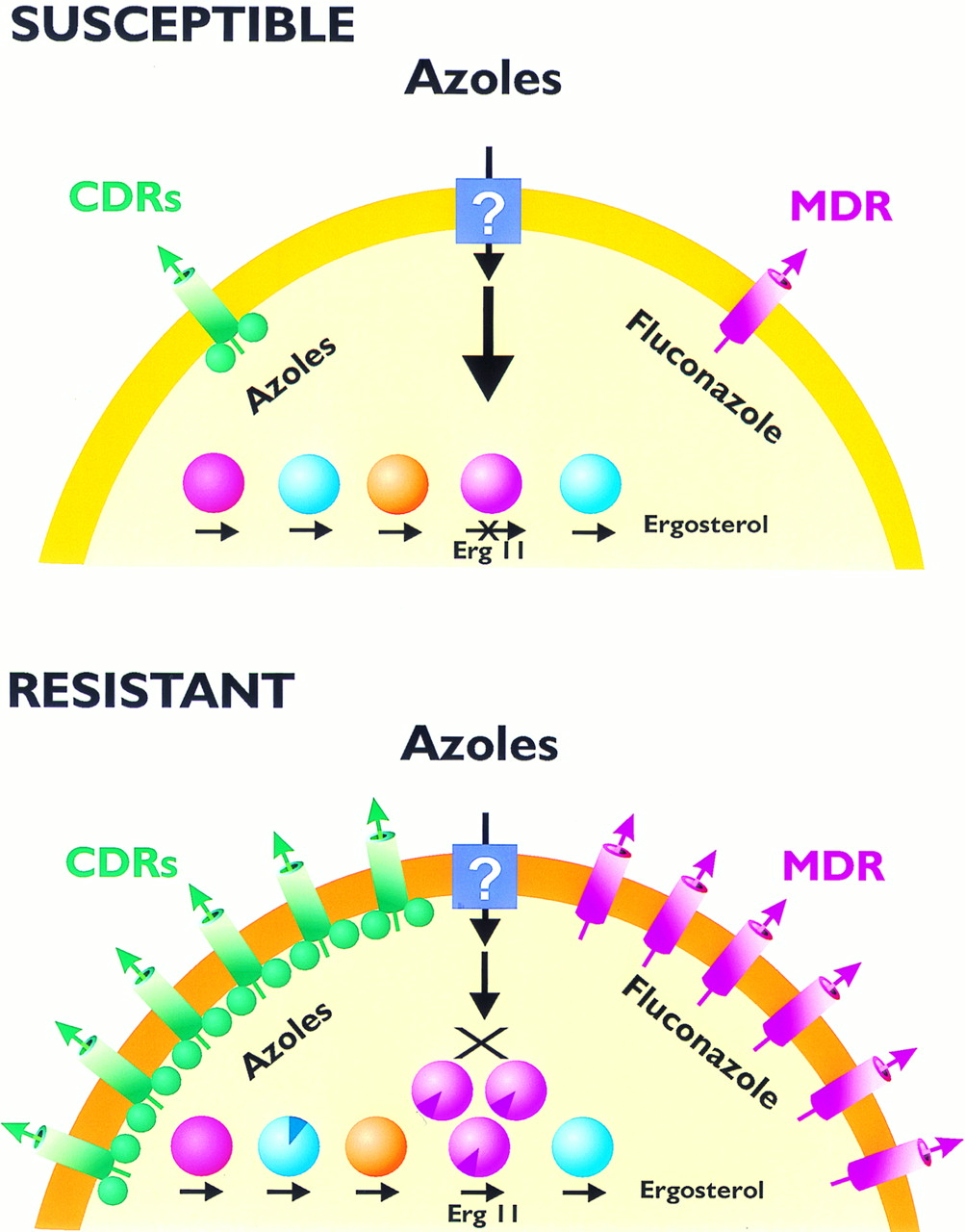
In spite of antifungal therapy have been improved in the past 30 years, the phenomenon of anti-fungal resistance is a major problem in clinical practice yet. Molecular mechanisms over the past 10 years, is associated with a phenomenon such as these are widely understood. In this paper, after a brief overview of the antifungal agents currently available, it will be described in detail molecular mechanisms of antifungal resistance. This is the main thing mechanism of resistance is something essential by deregulation of anti-fungal resistance effector gene was found. This deregulation is due to point mutations found in the transcriptional regulator of effector genes. I can resistor is monitored directly, point mutations in the gene encoding the antifungal target is generated. In addition, further, we describe a new strategy is performed to detect an alternative target for antifungal treatment and current. Identification of novel antifungal agents is accomplished by screening a collection of synthetic chemical compounds or natural. The discovery of antifungal estimation novel targets is performed by a whole genome approach to better understanding of pathogenic fungi in human biology.
Until recently, techniques for antifungal susceptibility testing has not been standardized. Laboratory Standards Institute Clinical and announced the reference method for susceptibility testing of yeast and fungi. These guidelines, we created a standard for comparison with clinical data. The European Commission for the study of sensitivity to antibiotics, has announced the guidelines for separation of Aspergillus and Candida test. However, doctors are faced with the challenge of how to interpret the results of the in vitro antifungal susceptibility test yet. MIC values are not associated with the response to direct treatment at all times. To predict treatment failure in vitro resistance HIV-infected patients, esophageal candidiasis or oral pharynx, but such a relationship has not been replicated in other settings. 90% of the cases is shown by the "rules of 60-90" says infections caused by susceptible strains, and corresponds to the appropriate treatment in, mismatch of in vitro data between in vivo and is resistant bacteria infections is an example% while the reaction at 60. Another limitation for determining the MIC is that MIC level is not the best indicator of resistance times. Some reports, minimum effective concentration is defined as the drug concentration resulted in a morphological change of the hyphal cells indicates that it may be more appropriate than MIC endpoint for susceptibility testing of filamentous bacteria echinocandin. In addition, infection antifungal activity of exposure to mold can detect conidia for activity against mycelial structure of many clinically important.
GENTAUR Belgium BVBA BE0473327336 Voortstraat 49, 1910 Kampenhout BELGIUM Tel 0032 16 58 90 45 Fax 0032 16 50 90 45 [email protected] GENTAUR Ltd. GB111298832 Howard Frank Turnberry House 1404-1410 High Road Whetstone London N20 9BH Tel 020 3393 8531 Fax 020 8445 9411 |
GENTAUR France SARL FR63484237888 9, rue Lagrange, 75005 Paris Tel 01 43 25 01 50 Fax 01 43 25 01 60 RCS Paris B 484 237 888 SIRET 48423788800017 RIB 30004 00187 00010092253 10 BNP PARIBAS PARIS PL MAUBERT BIC BNPAFRPPPRG IBAN FR76 3000 4001 8700 0100 9225 310 [email protected] |
GENTAUR GmbH DE815175831 Marienbongard 20 52062 Aachen Deutschland [email protected] Tel 0241 95 78 94 78 Tacka Vancheva Tel logistics 0241 4008 9086 Annick Verdeyen Fax 0241 55 91 05 36 Bankleitzahl 39050000 IBAN DE8839050000107569353 Handelsregister Aachen HRB16058 Steuernummer 201/5961/3925 [email protected] |
GENTAUR Nederland BV NL850396268B01 Kuiper 1 5521 DG Eersel Nederland KVK nummer 52327027 Tel: 0208-080893 Fax: 0497-517897 [email protected] IBAN: NL04RABO0156985462 SWIFT RABONL2U GENTAUR Ltd. GB111298832 Howard Frank Turnberry House 1404-1410 High Road Whetstone London N20 9BH Tel 020 3393 8531 Fax 020 8445 9411 |
GENTAUR U.S.A Genprice Inc, Logistics 547, Yurok Circle San Jose, CA 95123 Phone: (408) 472-2934 Fax:(408) 416-3994 Phone (718)513-2983 [email protected] Genprice Inc, Invoices and accounting 6017 Snell Ave San Jose, CA 95123 |
GENTAUR Italy 20135 Milano Tel 0236006593 Fax 0350085071 [email protected] GENTAUR Spain tel:0911876558 [email protected] GENTAUR BULGARIA BG20135893153, Graf Ignatiev Str. ent.V, fl. 2 Sofia 1000 Tel 0035929830070 Fax 0035929830072 [email protected] |
ГЕНТАУЪР БЪЛГАРИЯ ID # 201 358 931 BULSTAT София 1000 ул. "Граф Игнатиев" 53 вх. В, ет. 2 Tel 0035929830070 Fax 0035929830072 e-mail: [email protected] IBAN: BG11FINV91501014771636 BIC: FINVBGSF |
Other countries Österreich +43720880899 Canada Montreal +15149077481 Ceská republika Praha +420246019719 Danmark +4569918806 Finland Helsset +358942419041 Magyarország Budapest +3619980547 Ireland Dublin +35316526556 Luxembourg +35220880274 Norge Oslo +4721031366 Sverige Stockholm +46852503438 Schweiz Züri +41435006251 US New York +17185132983 |