 |
 |
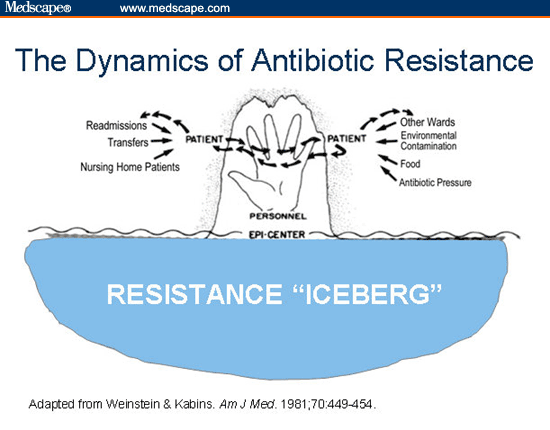
Many viruses survived for thousands of years on the ability of various microorganisms to adapt to antimicrobial agents. By spontaneous mutation, they do this or by DNA transfer. This process can be disabled antibiotics rendering some bacteria to resist the action of certain antibiotics. These microorganisms utilize several mechanisms to achieve a plurality of drug resistance:
- No longer relying on the cell wall of glycoprotein
- Enzyme inactivation of antibiotics
- Reducing the permeability of the cell wall of antibiotics
- Site was changed to a target of the antibiotic
- For removal of the antibiotic, release mechanism
- Increase in the Mutation rate in response to stress
Bacteria in many different shows multi-drug resistance, such as tuberculosis and Gram-negative bacteria and many other staphylococci, enterococci, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Streptococcus, Salmonella and, now. Can be passed to the resistance gene subsequently resistant bacteria some copies of the DNA encoding the mechanisms of resistance to related species, closely other bacteria, which confers resistance to their neighbors thereby you can transfer. This process is called horizontal gene transfer.
Antibiotic resistance is regarded as one of the greatest problems of modern public health care. More and more cases of bacteria resistance to drugs have been registered in the last decade. A great deal of the known viruses are slowly building their protection against the most common antibiotics. It has been proven that some microbes are killed after taking antibiotics. However, it is also known that others are left alive and they continue to multiply. Drug Resistance is usually caused by using antibiotics in an inadequate way or in inordinate quantities. Abusing the effects of antibiotics jeopardises their benefits in future treatments. Such misuse should be avoided in order to control drug resistance. Children comprise one of the most vulnerable groups,because their treatment includes antibiotics in almost every case. The danger is greatest for people, who have been using antibiotics to cope with infections. When the antibiotics fail to work after a while, the outcomes are drastic. People will be faced with diseases that remain incurable for long periods of time. Furthermore, they will have to visit their physicians more often or even increase the number of visits they pay to hospitals. Some patients may require more expensive or toxic drugs. Such conditions may end even in death.

Causes for Antibiotic Drug Resistance
Widespread use of antibiotics, there is a low-level presence of resistant bacteria in the evolution of pressure before played a role in the development of multidrug-resistant varieties, to use the spread of resistance of bacterial species between them. In medicine, the main problem of the emergence of drug-resistant strains of bacteria is due to overuse and inappropriate use of antibiotics. I only sell antibiotics without a prescription without a prescription lead to the creation of resistant strains in some countries. Other practices that contribute to resistance include the addition of antibiotics to animal feed. Domestic use of antimicrobial products similar to the soap, it has not been contributing to the resistance obviously but (it is not effective in the control of infectious diseases) is avoided. And also unhealthy practices in the pharmaceutical industry, may contribute to the possibility of creating a clinical practice and tolerance strains.The procedure during the period of the drawbacks medication often - they prevent the patient or to prevent re-infection infection of new pathogens are not taken to, refuse to complete destruction objective by the end of the course. Several classes of antibiotics is correlated with colonization "super bug" as compared to other classes of antibiotics very. Superbug known as multidrug resistance, is a bacterium carrying the resistance gene few. In addition, the organization, use the antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action against "good bacteria", if there is a (resistance), the risk of colonization, the higher the lack of sensitivity of the super bug of high penetration . In the case of MRSA, the increase of MRSA infection levels, seen glycopeptides, quinolones, cephalosporins in, in particular. It is included in the clindamycin and quinolones and certain cephalosporins in the case of colonization of Clostridium difficile antibiotic detection risk. Of the antibiotics used in the United States in 1997, half is used for humans and animals in half.
GENTAUR Belgium BVBA BE0473327336 Voortstraat 49, 1910 Kampenhout BELGIUM Tel 0032 16 58 90 45 Fax 0032 16 50 90 45 [email protected] GENTAUR Ltd. GB111298832 Howard Frank Turnberry House 1404-1410 High Road Whetstone London N20 9BH Tel 020 3393 8531 Fax 020 8445 9411 |
GENTAUR France SARL FR63484237888 9, rue Lagrange, 75005 Paris Tel 01 43 25 01 50 Fax 01 43 25 01 60 RCS Paris B 484 237 888 SIRET 48423788800017 RIB 30004 00187 00010092253 10 BNP PARIBAS PARIS PL MAUBERT BIC BNPAFRPPPRG IBAN FR76 3000 4001 8700 0100 9225 310 [email protected] |
GENTAUR GmbH DE815175831 Marienbongard 20 52062 Aachen Deutschland [email protected] Tel 0241 95 78 94 78 Tacka Vancheva Tel logistics 0241 4008 9086 Annick Verdeyen Fax 0241 55 91 05 36 Bankleitzahl 39050000 IBAN DE8839050000107569353 Handelsregister Aachen HRB16058 Steuernummer 201/5961/3925 [email protected] |
GENTAUR Nederland BV NL850396268B01 Kuiper 1 5521 DG Eersel Nederland KVK nummer 52327027 Tel: 0208-080893 Fax: 0497-517897 [email protected] IBAN: NL04RABO0156985462 SWIFT RABONL2U GENTAUR Ltd. GB111298832 Howard Frank Turnberry House 1404-1410 High Road Whetstone London N20 9BH Tel 020 3393 8531 Fax 020 8445 9411 |
GENTAUR U.S.A Genprice Inc, Logistics 547, Yurok Circle San Jose, CA 95123 Phone: (408) 472-2934 Fax:(408) 416-3994 Phone (718)513-2983 [email protected] Genprice Inc, Invoices and accounting 6017 Snell Ave San Jose, CA 95123 |
GENTAUR Italy 20135 Milano Tel 0236006593 Fax 0350085071 [email protected] GENTAUR Spain tel:0911876558 [email protected] GENTAUR BULGARIA BG20135893153, Graf Ignatiev Str. ent.V, fl. 2 Sofia 1000 Tel 0035929830070 Fax 0035929830072 [email protected] |
ГЕНТАУЪР БЪЛГАРИЯ ID # 201 358 931 BULSTAT София, Кокаляне 1191 ул. "Искър" 53 вх. В, ет. 2 Tel 0035929830070 Fax 0035929830072 e-mail: [email protected] IBAN: BG11FINV91501014771636 BIC: FINVBGSF |
Other countries Österreich +43720880899 Canada Montreal +15149077481 Ceská republika Praha +420246019719 Danmark +4569918806 Finland Helsset +358942419041 Magyarország Budapest +3619980547 Ireland Dublin +35316526556 Luxembourg +35220880274 Norge Oslo +4721031366 Sverige Stockholm +46852503438 Schweiz Züri +41435006251 US New York +17185132983 |